Medications like Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Trulicity have recently boomed in popularity. Originally approved to treat obesity and type 2 diabetes, these medications, commonly known as GLP-1 agonists, are increasingly being used to aid in general weight loss. In fact, 1 in 8 adults reports having taken a GLP-1 medication.
GLP-1 medications are becoming more prevalent due to the changes in appetite and digestion they cause, often resulting in rapid weight loss. With the right exercise regimen and nutritional plans, GLP-1s can be a safe and effective option for those who need to lose weight, but it’s important to understand how these medications affect your body — and how to best support it when you’re taking a GLP-1.
If you’re considering whether a GLP-1 medication is right for you, understanding your nutritional needs and how GLP-1 medications may affect them is critical to achieving sustainable results.
Let’s talk about:
- GLP-1s and nutrition
- Calorie counting vs. nutrient density
- How much protein to eat on a GLP-1 diet
- The best GLP-1 foods to meet your nutritional needs
- How to measure success on a GLP-1 nutrition plan
What are GLP-1s?
GLP-1 drugs, also known as GLP-1 agonists, are medications that are designed to manage blood sugar levels and treat obesity. GLP-1 is a naturally occurring hormone that controls several functions in your body, including:
- Insulin release
- Glucose level control
- Digestion
- Hunger and fullness signaling
GLP-1 medications work by mimicking the natural hormone and binding to GLP receptors to trigger its effects. When taking a GLP-1 drug, it’s important to support your body with regular exercise — such as resistance training — and a nutrient-dense diet.
How GLP-1s affect eating habits
Because GLP-1 drugs slow down your body’s natural digestion processes, those who take GLP-1 medications tend to feel full longer and eat less overall. Over time, eating fewer calories than you burn in a day generally leads to fat loss — but when GLP-1 drugs are involved, meeting your nutritional needs takes extra care.
GLP-1s and nutrition
When you may be less in tune with your body’s hunger and fullness cues, remembering to eat throughout the day and meeting your body’s macronutrient and micronutrient needs can be challenging. While eating fewer calories aids in weight loss, a severe lack of nutrition or a calorie intake that’s too low can lead to unwanted health effects, such as:
- Mood swings
- Low energy levels
- Poor digestion
- Frequent illness
- Skin and hair problems
Taking GLP-1s can also lead to muscle loss and make it more difficult to maintain muscle mass, which keeps your body functioning properly. That’s why understanding GLP-1 nutrition is key to long-term success and sustainable results if you’re taking medication to support weight loss.
What is the best diet for GLP-1?
While there isn’t a “best” GLP-1 diet plan, Gianna Masi, RDN, CISSN, CPT, Stronger U Nutrition dietitian, says, “Having baseline targets of protein, fiber, and calories is important for those on GLP-1s to maintain muscle mass and reduce the risk of muscle loss or nutrient deficiencies.”
GLP-1 nutrition plans will vary from person to person, based on their individual weight loss goals, current nutritional intake, and personal preferences. That said, Masi has a few strategies and tips to keep in mind when planning what to eat on a GLP-1 diet.
Nutrient density vs. calorie count
Counting calories is a common practice on a weight-loss diet, but it looks a little different for someone who is taking a GLP-1 medication. Masi says, “GLP-1 medications help support getting into a significant caloric deficit to lose weight. For this reason, many may still count calories as a way to ensure they’re not under-eating [and maintaining] baseline energy needs.”
But consuming enough calories is only one part of the GLP-1 nutrition puzzle — it’s also important to focus on nutrient density. Masi adds, “Nutrient density is always essential but becomes even more critical when we’re unable to eat as much food volume as we’re used to. This means we may under-eat foods with key macro and micronutrients for optimal health and fitness.” Eating a nutrient-dense diet helps prevent deficiencies and supports body processes like digestion.
To meet your energy needs without filling up too fast, Masi suggests eating low volumes of nutrient-dense foods. Here’s an example: Instead of eating 1.25 cups of cereal (high volume, 140 calories), opt for ⅓ cup of granola (low volume, 140 calories).
“By eating the lower-volume foods, you can still achieve your calorie and nutrient needs but with less volume in your stomach, making it more attainable to eat enough,” Masi says.
How much protein to eat on GLP-1
Protein is one of the key macronutrients your body needs to function properly — and build and maintain muscle mass — so it’s especially important on a GLP-1 diet.
To determine the optimal amount of protein for a GLP-1 nutrition plan, Masi recommends calculating a daily range to aim for. Your recommended range can be calculated by multiplying your goal body weight by .7 to get the lower end of the target of how many grams of protein you need per day. Then, multiply your goal weight by 1 to determine the upper end of your target range. For example: If your goal weight is 150 pounds, aim for 105–150 grams of protein per day.
In addition to protein, she says it’s important to consume key nutrients like dietary fat, fiber, micronutrients, and carbohydrates for performance.
Protein sources for a GLP-1 meal plan
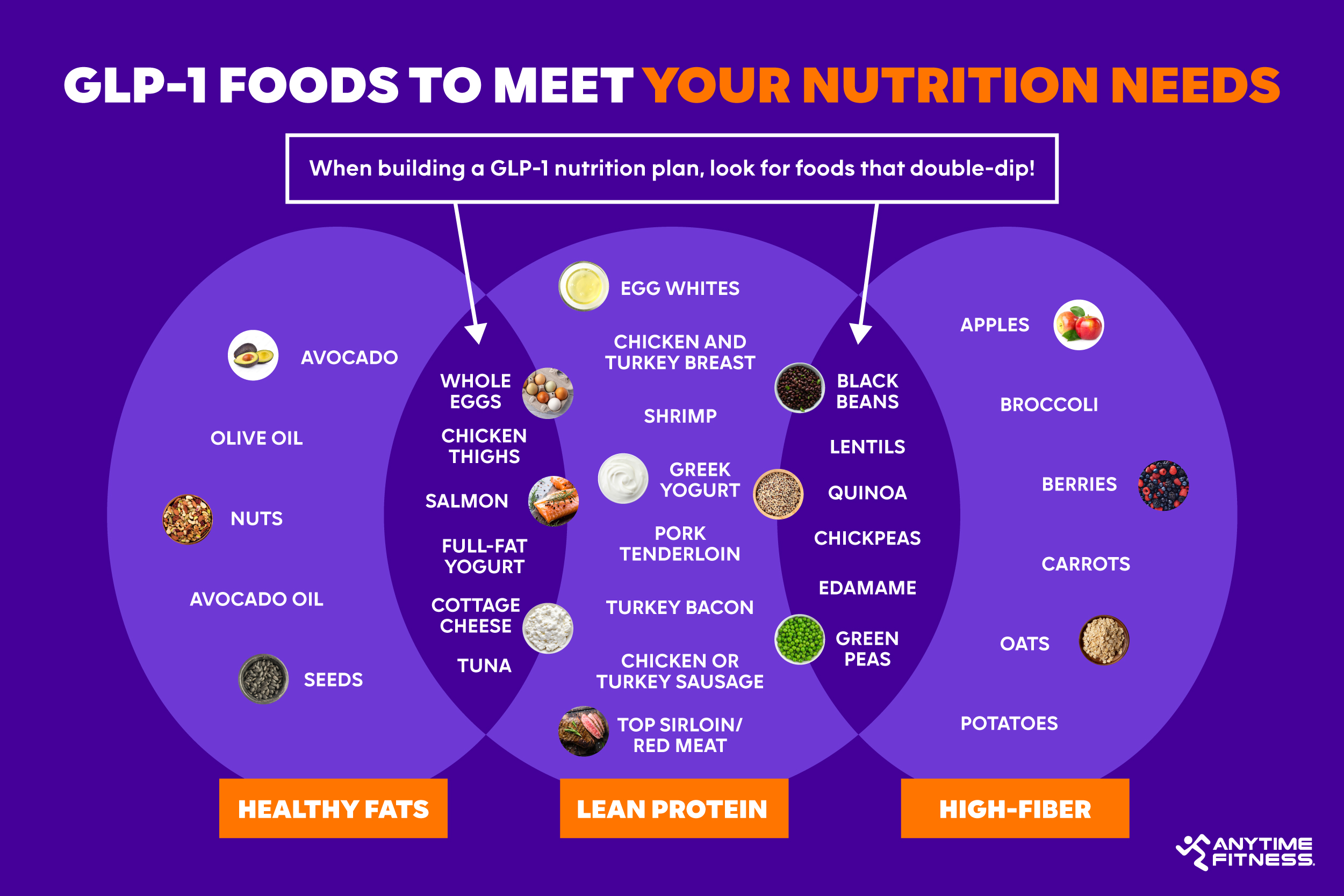
To meet your baseline protein needs, it’s a good practice to identify your favorite — or most tolerable — protein sources while on medication. Some of the best lean protein sources include:
- Egg whites
- Chicken and turkey breast
- Shrimp
- Pork tenderloin
- Greek yogurt
- Turkey bacon
- Chicken or turkey sausage
- Top sirloin/lean red meat
Other good protein sources — especially for those who eat vegan or vegetarian — include tofu, tempeh, seitan, and plant-based protein powders.
The importance of hydration
Hydration is an essential part of any diet — every cell, tissue, and organ in your body depends on water to carry out its job. But staying hydrated on a GLP-1 medication can be more difficult due to delayed gastric emptying and earlier feelings of fullness. Plus, GLP-1 medications may lead to gastrointestinal side effects like constipation or diarrhea that can result in dehydration.
Masi advises prioritizing hydration early and often to stay on top of your daily needs and support your body’s functions. Your goal amount depends on many factors, including your activity level. The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends this routine:
- Drink 17–20 ounces of water 2–3 hours before you start exercising.
- Drink 8 ounces of water 20–30 minutes before you start exercising or during your warm-up.
- Drink 7–10 ounces of water every 10–20 minutes during exercise.
- Drink 8 ounces of water no more than 30 minutes after you exercise.
Best GLP-1 foods for meeting your nutritional needs
Since consuming enough calories and nutrients can be challenging on a GLP-1 diet, Masi suggests combining fat and protein sources together to reach your daily targets. She says some of the best GLP-1 foods to achieve protein and fat targets include:
- Whole eggs
- Chicken thighs
- Salmon
- Lean steak/beef
- Full-fat cottage cheese
- Tuna
- Full-fat yogurt
In addition to protein and fat, Masi emphasizes the need for fiber, which helps regulate digestive health, cholesterol levels, blood sugar, gut health, and fullness. While options for high-fiber, high-protein meals are endless when you combine a protein source with a fruit, vegetable, or whole grain, there are also foods that are good sources of both. Here are a few examples, including the amount of protein and fiber per cup:
- Lentils: 18 grams protein, 15 grams fiber
- Chickpeas: 15 grams protein, 12 grams fiber
- Black beans: 15 grams protein, 15 grams fiber
- Edamame: 17 grams protein, 8 grams fiber
- Quinoa: 8 grams protein, 5 grams fiber
- Green peas: 9 grams protein, 9 grams fiber
3 tips for planning meals on a GLP-1 diet
While GLP-1 meal plans vary from person to person, there are three key tips to keep in mind to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs.
- Include protein and color from a high-fiber source like a fruit or vegetable in your meals to cover your baseline protein, fiber, and micronutrient needs.
- Monitor the total energy (calories) you’re taking in throughout the day. You may want to eat smaller, more frequent meals or snacks to reach your daily calorie goals. You’ll feel stronger and have more energy when you’re consuming your daily calorie needs.
- Consider consulting a dietitian or physician. Working with a registered dietitian or a medical professional can help maximize your performance and results — and manage symptoms — when taking a GLP-1. They can help personalize your GLP-1 nutrition plan based on your current diet, weight loss goals, and preferences.
How to measure success on a GLP-1 diet
Weight loss journeys are personal, and each one is different. Over time, combining a GLP-1 medication with regular exercise and a nutrient-dense diet can aid in weight loss — but the number on the scale isn’t the only measure of your success.
You may also notice feeling stronger during workouts, increasing sets, reps, or weight. You may be able to walk, bike, or run the same distance in less time — or go further than before. Other non-scale victories include how clothes are fitting, your body measurements, and a shift in your mindset and self-confidence. A weight-loss journey is an investment in yourself, and you’ve got a lot to celebrate!

A final word on GLP-1 nutrition
Masi puts it this way: “A common misconception is that using GLP-1 medications is simply ‘taking the easy way out.’ In reality, these medications exist for a reason, and for eligible individuals, they provide an option to be considered carefully.” While taking GLP-1 medications, it’s important to emphasize resistance training and proper nutrition to support your goals.
Working with a trusted provider can help you weigh the pros and cons of taking GLP-1s with your personal health goals. If you decide GLP-1s are the right path for you, a registered dietitian can help you strategize and implement the best GLP-1 nutrition plan for you — one that leads to sustainable results and helps you feel your best.
More nutrition and weight loss resources
Get connected with an Anytime Fitness Coach for personalized training, nutrition, and recovery guidance to support your weight loss goals.



